Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 7
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 março 2025
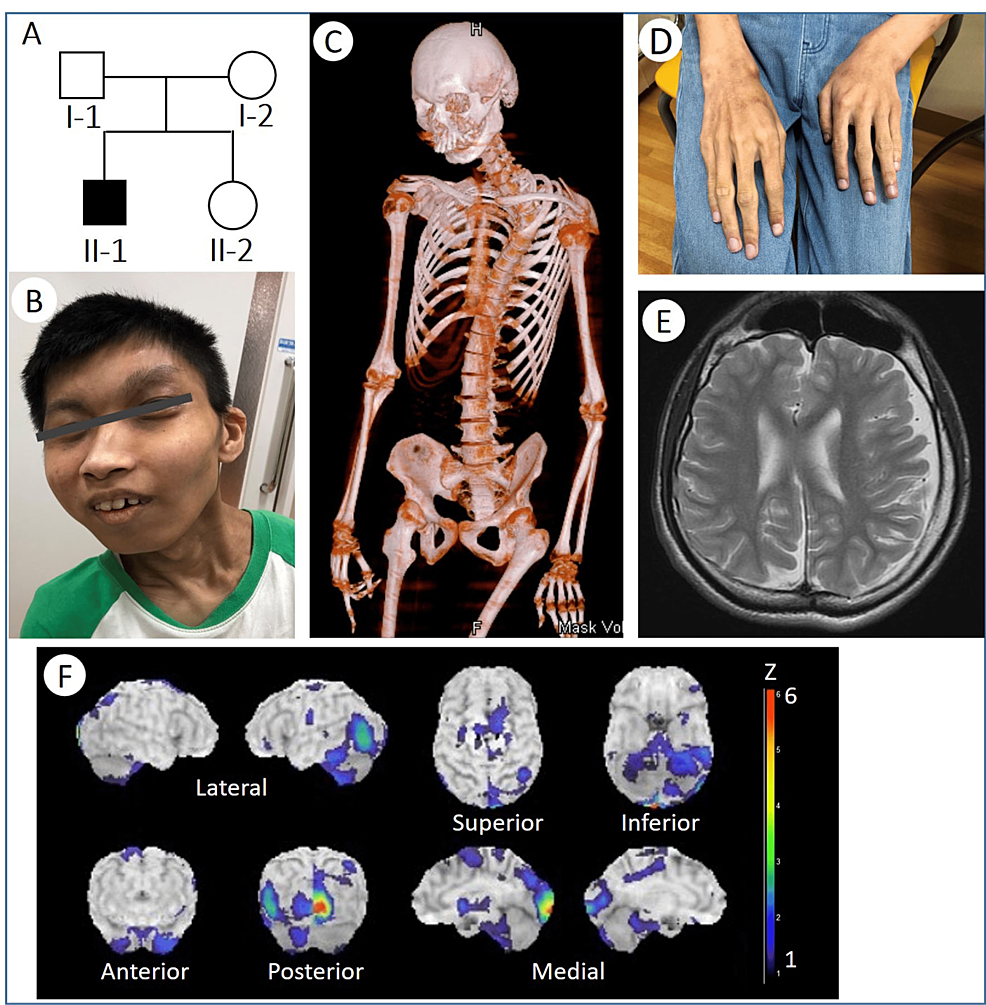
Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7 (MRD7; OMIM 614104) is a rare disease characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, speech delay, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphisms. This disorder is caused by pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants of the DYRK1A gene, which encodes dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A. Here, we report a case of MRD7 that was diagnosed using Face2Gene and whole-exome sequencing (WES). A 22-year-old man presented with microcephaly, intellectual disability, slender body, long slender fingers, and facial dysmorphisms. He was previously diagnosed with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) at four years of age. However, his CdLS clinical diagnostic score was low at 22 years of age. The Face2Gene application introduced several candidate diseases including MRD7. Finally, by utilizing WES and Sanger sequencing analysis of cloned cDNA, we identified a novel heterozygous duplication variant (c.848dup, p.(Asn283LysfsTer6)) in the DYRK1A gene, which introduces a premature stop codon. This report provides more information about the phenotypic spectrum of a young adult patient with MRD7. Face2Gene helped us introduce candidate diseases of the patient. Registering further genetically confirmed cases with MRD7 will improve the accuracy of the diagnostic recommendations in Face2Gene. Moreover, WES is a powerful tool for diagnosing rare genetic diseases, such as MRD7.

Truncation of the Down syndrome candidate gene DYRK1A in two unrelated patients with microcephaly. - Abstract - Europe PMC

PDF) Case report of a syndromic girl with intellectual disability having both DYRK1A and SCN1A mutation
Pitfalls of whole exome sequencing in undefined clinical conditions with a suspected genetic etiology
Whole exome sequencing reveals putatively novel associations in retinopathies and drusen formation

Clinical Whole-Exome Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Mendelian Disorders
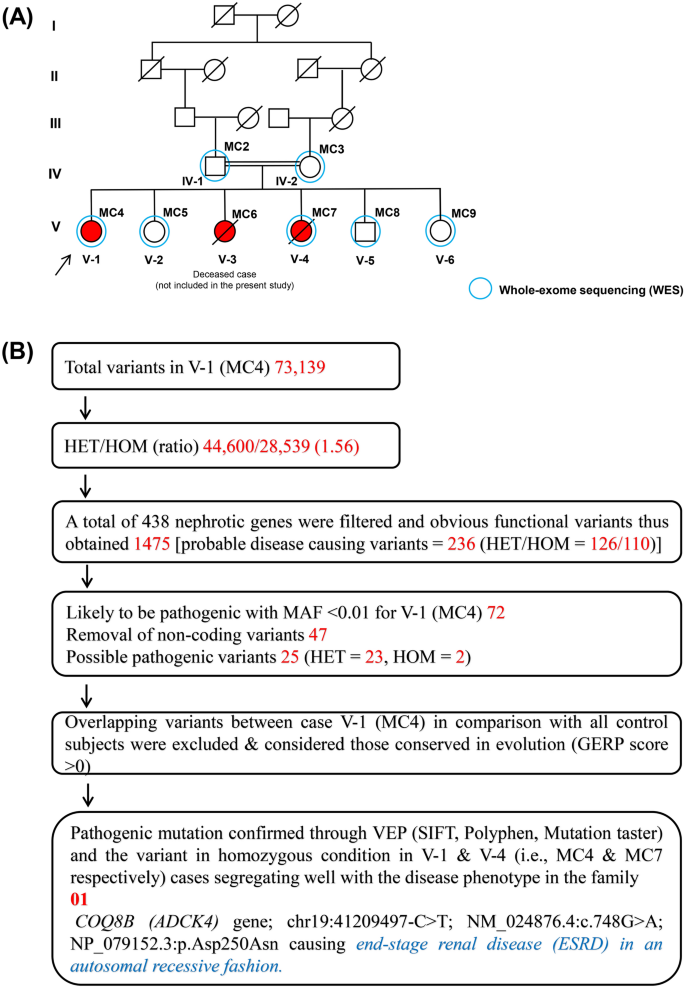
Whole-exome sequencing reveals a novel homozygous mutation in the COQ8B gene associated with nephrotic syndrome

Integrative approach to interpret DYRK1A variants, leading to a frequent neurodevelopmental disorder
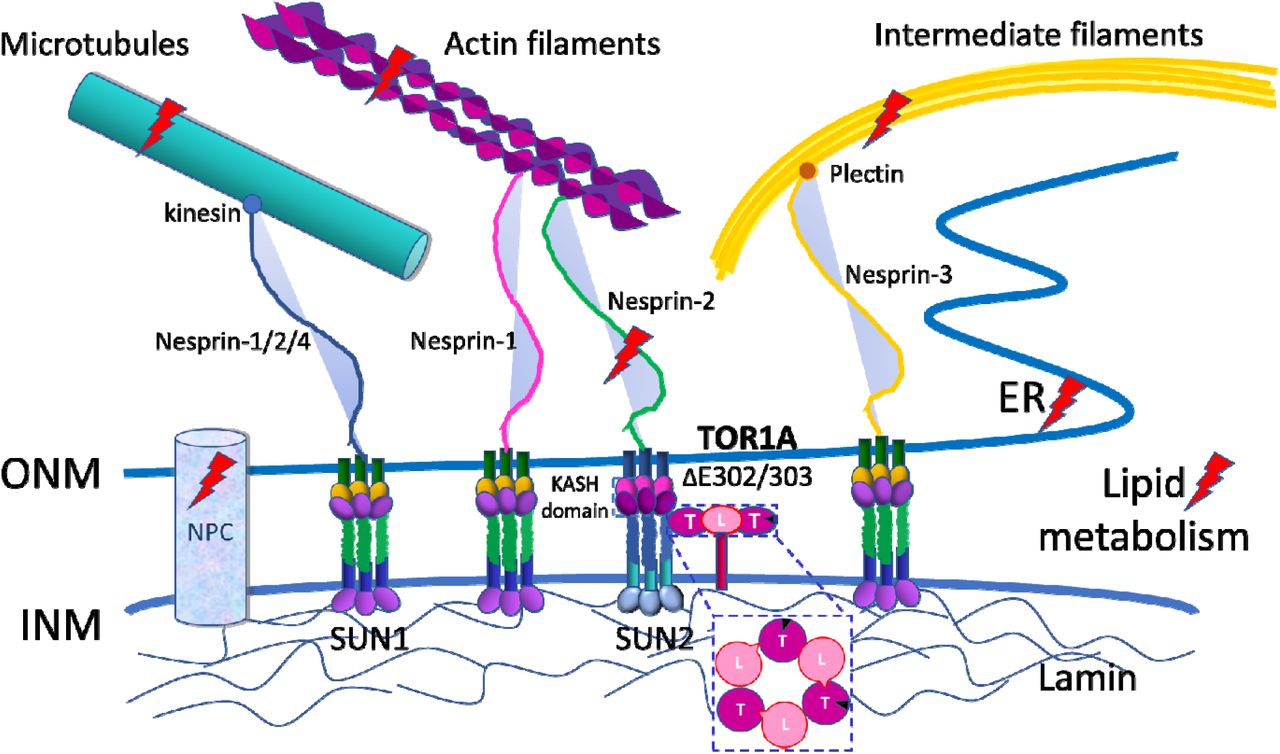
Whole exome sequencing identifies novel DYT1 dystonia-associated genome variants as potential disease modifiers

De Novo Disruption of the Proteasome Regulatory Subunit PSMD12 Causes a Syndromic Neurodevelopmental Disorder. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Recomendado para você
-
 Anaesthesia Management in a Child with Rubinstein - Taybi Syndrome22 março 2025
Anaesthesia Management in a Child with Rubinstein - Taybi Syndrome22 março 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025 -
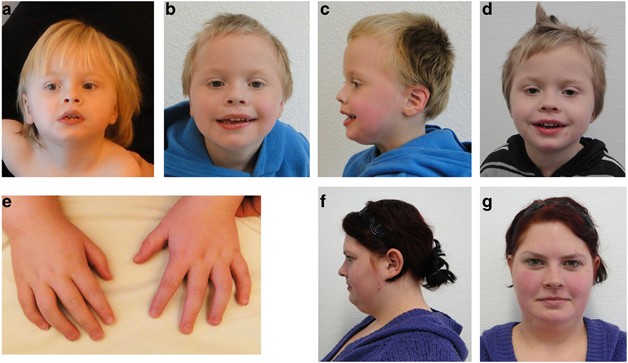
![Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114458/bin/fhs-Image002.jpg) Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025
Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials22 março 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials22 março 2025 -
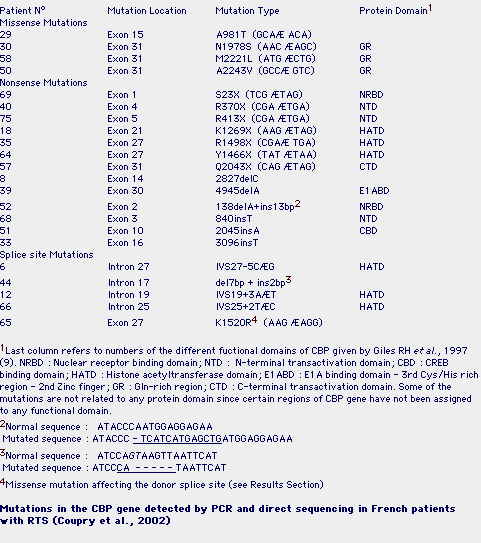
 A mosaic maternal splice donor mutation in the EHMT1 gene leads to aberrant transcripts and to Kleefstra syndrome in the offspring22 março 2025
A mosaic maternal splice donor mutation in the EHMT1 gene leads to aberrant transcripts and to Kleefstra syndrome in the offspring22 março 2025 -
 Floating-Harbor syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics22 março 2025
Floating-Harbor syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics22 março 2025 -
 genereviews.org - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025
genereviews.org - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025 -
 Silver Russell Syndrome: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews22 março 2025
Silver Russell Syndrome: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews22 março 2025 -
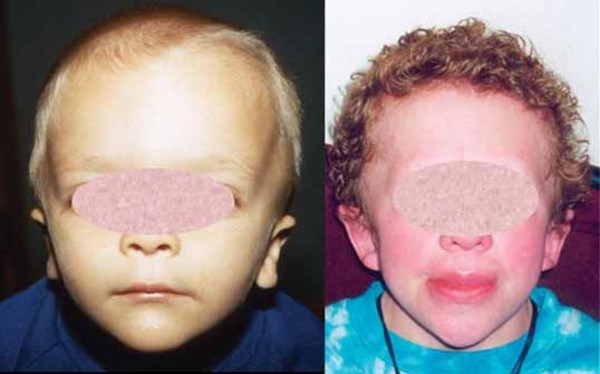
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS)22 março 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS)22 março 2025 -
 Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Faiyaz EFAZ, Student, Bachelor of Science in Chemistry, University of Chittagong, Chittagong, Department of Chemistry22 março 2025
Faiyaz EFAZ, Student, Bachelor of Science in Chemistry, University of Chittagong, Chittagong, Department of Chemistry22 março 2025 -
 Yofukashi No Uta Call Of The Night GIF - Yofukashi No Uta Call Of22 março 2025
Yofukashi No Uta Call Of The Night GIF - Yofukashi No Uta Call Of22 março 2025 -
 Tokyo Ghoul - Volume 1 (Portuguese Edition22 março 2025
Tokyo Ghoul - Volume 1 (Portuguese Edition22 março 2025 -
 Catherine Full Body Heart's Desire Premium Edition - Video Game Shelf22 março 2025
Catherine Full Body Heart's Desire Premium Edition - Video Game Shelf22 março 2025 -
 Yu yu hakusho 2018 OVA 1 e 2 HD22 março 2025
Yu yu hakusho 2018 OVA 1 e 2 HD22 março 2025 -
 Save 40% on DRAGON QUEST® XI S: Echoes of an Elusive Age22 março 2025
Save 40% on DRAGON QUEST® XI S: Echoes of an Elusive Age22 março 2025 -
![Tomodachi game - [Chap 119] - [Chap mới nhất 119] TRUYENGIHOT](https://s3-ap-northeast-2.cdnimgtgh.com/tomodachi-game-m/119/036.jpg) Tomodachi game - [Chap 119] - [Chap mới nhất 119] TRUYENGIHOT22 março 2025
Tomodachi game - [Chap 119] - [Chap mới nhất 119] TRUYENGIHOT22 março 2025 -
 Millwall fixtures for Championship 2023/24 season: Middlesbrough away begins optimistic campaign22 março 2025
Millwall fixtures for Championship 2023/24 season: Middlesbrough away begins optimistic campaign22 março 2025 -
 Argentina - Club Atlético de la Juventud Alianza - Results22 março 2025
Argentina - Club Atlético de la Juventud Alianza - Results22 março 2025 -
 Pacote Artes Times Brasileiros 2021-22 Vetor Camisas22 março 2025
Pacote Artes Times Brasileiros 2021-22 Vetor Camisas22 março 2025