Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 01 abril 2025

Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) is a growth disorder variably characterized by macroglossia, hemihyperplasia, omphalocele, neonatal hypoglycemia, macrosomia, embryonal tumors (e.g., Wilms tumor, hepatoblastoma, neuroblastoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma), visceromegaly, adrenocortical cytomegaly, kidney abnormalities (e.g., medullary dysplasia, nephrocalcinosis, and medullary sponge kidney), and ear creases / posterior helical ear pits. BWS is considered a clinical spectrum, in which affected individuals may have many or only one or two of the characteristic clinical features. Although most individuals with BWS show rapid growth in late fetal development and early childhood, growth rate usually slows by age seven to eight years. Adult heights are typically within the normal range. Hemihyperplasia (also known as lateralized overgrowth) is often appreciated at birth and may become more or less evident over time. Hemihyperplasia may affect segmental regions of the body or selected organs and tissues. Hemihyperplasia may be limited to one side of the body (ipsilateral) or involve opposite sides of the body (contralateral). Macroglossia is generally present at birth and can obstruct breathing or interfere with feeding in infants. Neonatal hypoglycemia occurs in approximately 50% of infants with BWS; most episodes are mild and transient. However, in some cases, persistent hypoglycemia due to hyperinsulinism may require consultation with an endocrinologist for therapeutic intervention. With respect to the increased risk for embryonal tumor development, the risk for Wilms tumor appears to be concentrated in the first seven years of life, whereas the risk for developing hepatoblastoma is concentrated in the first three to four years of life. Cognitive and neurobehavioral development is usually normal. After childhood, prognosis is generally favorable, although some adults experience issues requiring medical management (e.g., for renal or skeletal concerns).

Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: Causes, symptoms, treatment, and more

Phenotype evolution and health issues of adults with Beckwith
Uniparental Disomy of Chromosome 11 disease: Malacards - Research
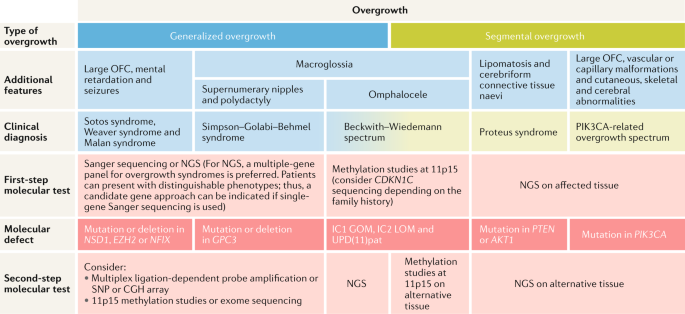
Overgrowth syndromes — clinical and molecular aspects and tumour

Role of epigenetics in Rett syndrome

GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf
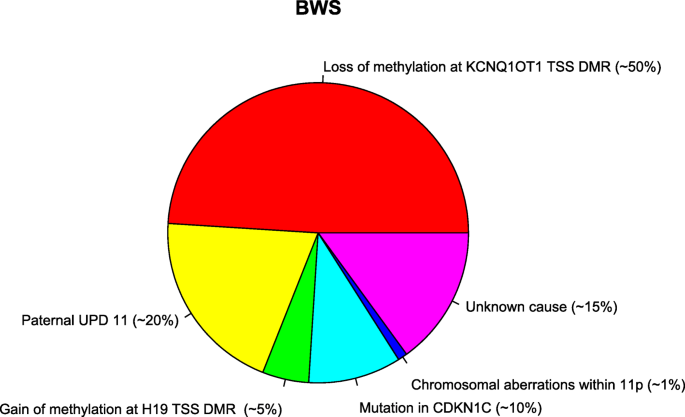
Genome-wide methylation profiling of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
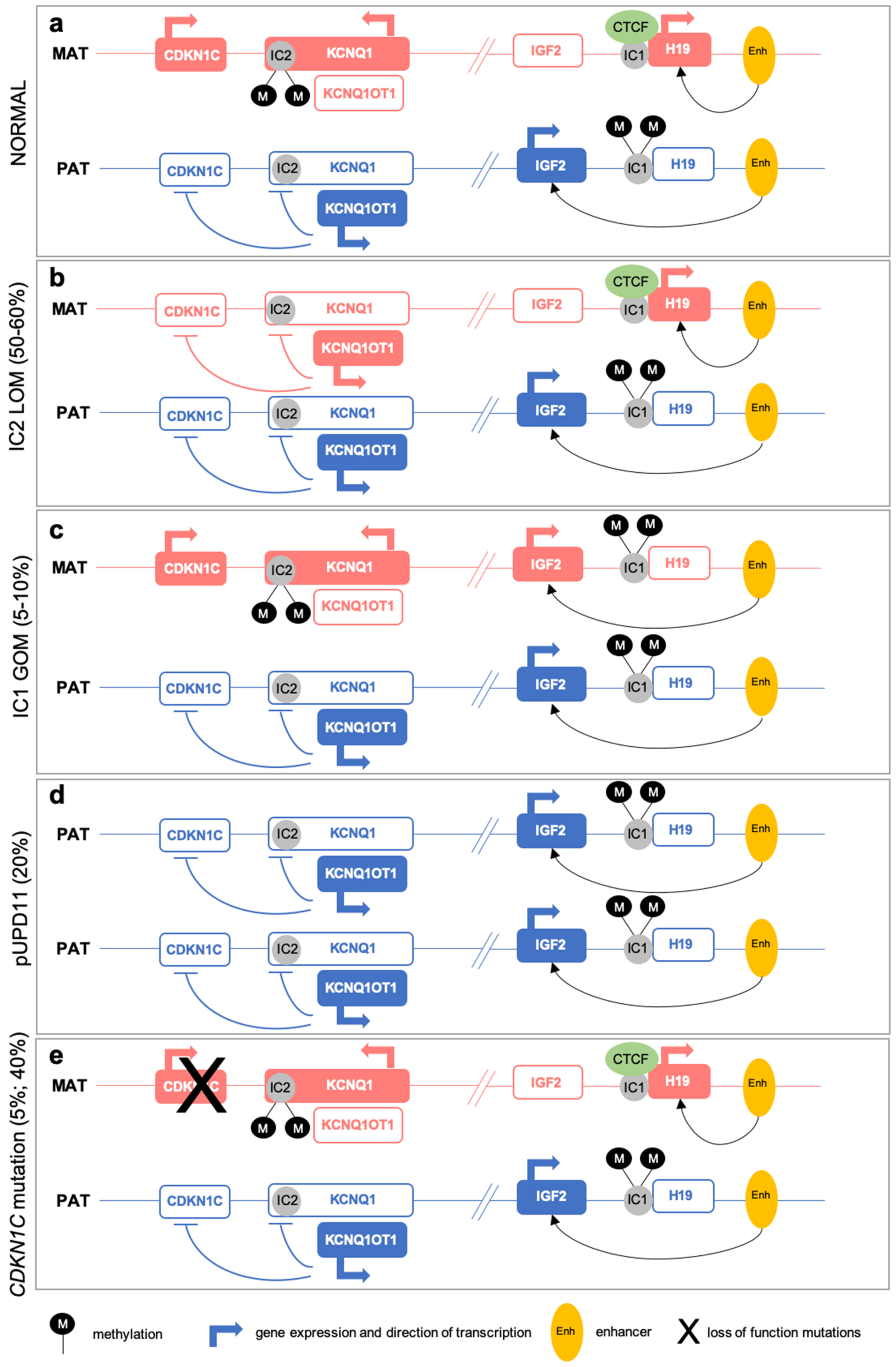
IJMS, Free Full-Text
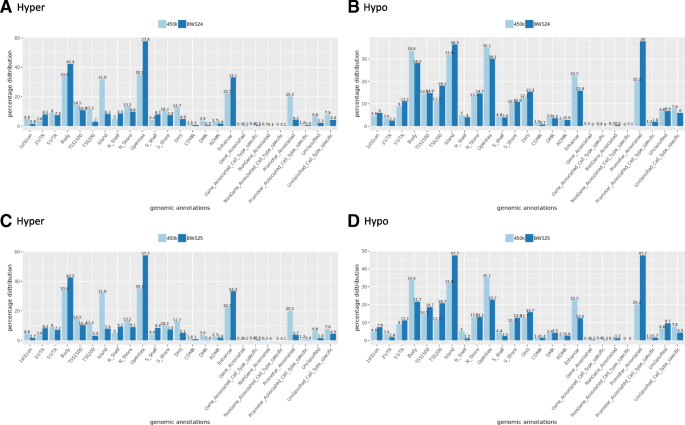
Genome-wide methylation profiling of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
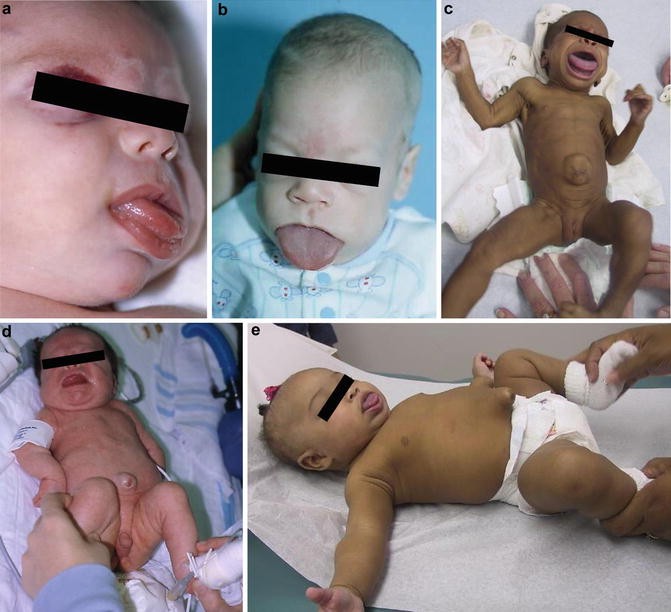
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
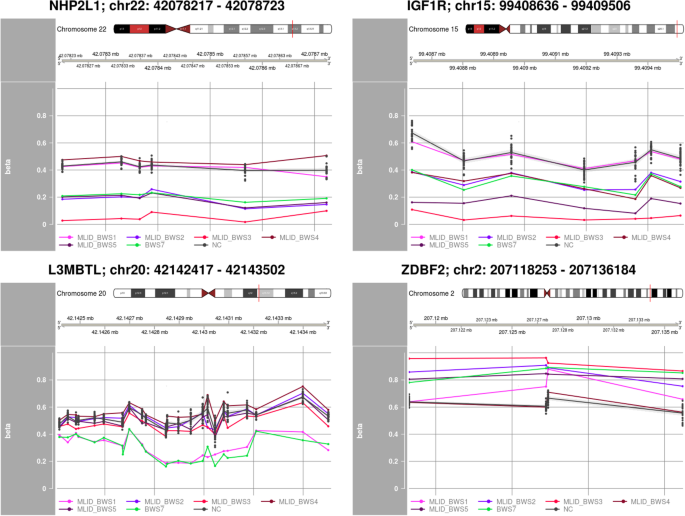
Genome-wide methylation profiling of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome

Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome by Carlos Jimenez
GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf
Recomendado para você
-
 Forgotten Diseases Research Foundation01 abril 2025
Forgotten Diseases Research Foundation01 abril 2025 -
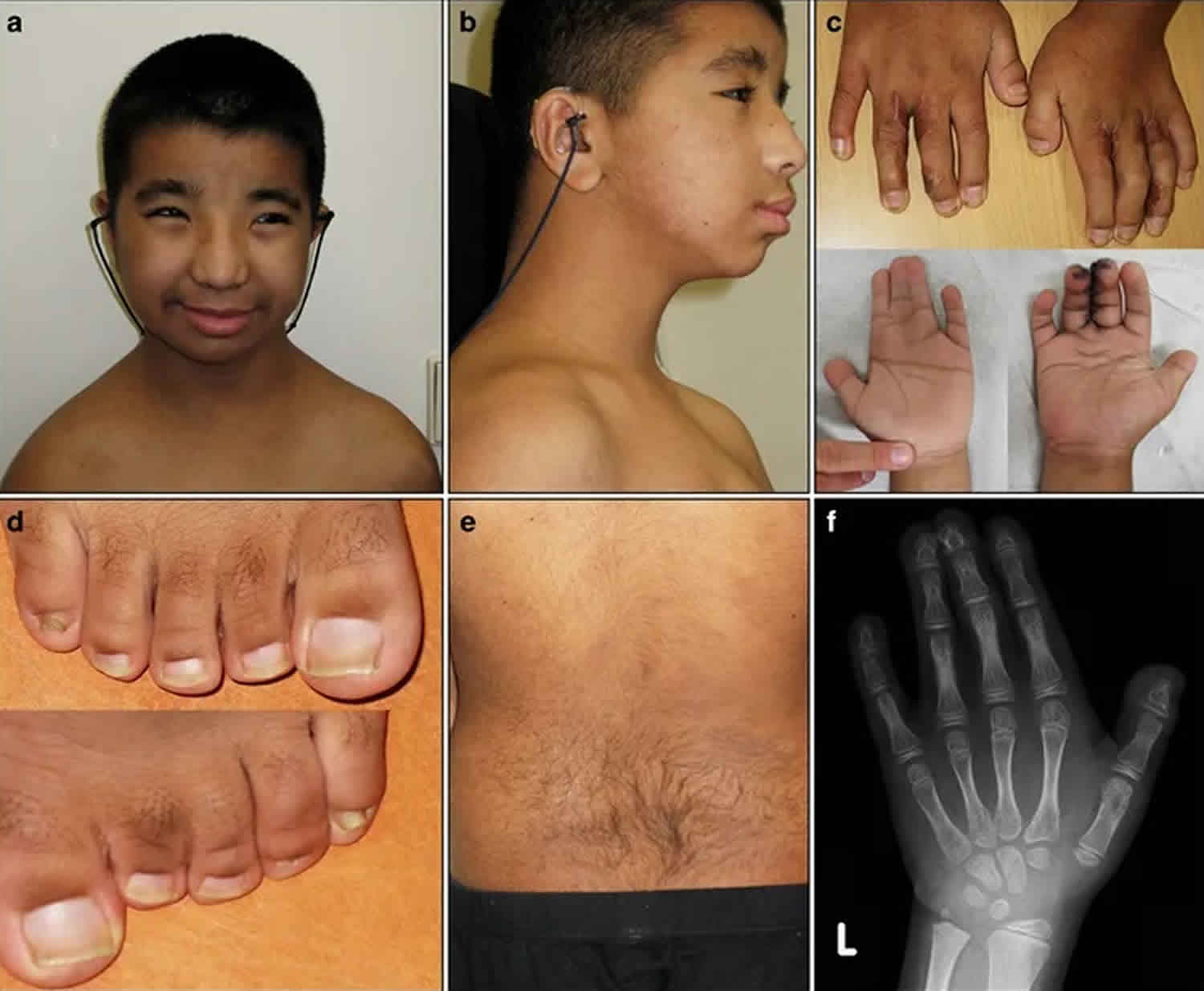 Rubinstein Taybi syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis01 abril 2025
Rubinstein Taybi syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis01 abril 2025 -
![Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114458/bin/fhs-Image001.jpg) Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf01 abril 2025
Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf01 abril 2025 -
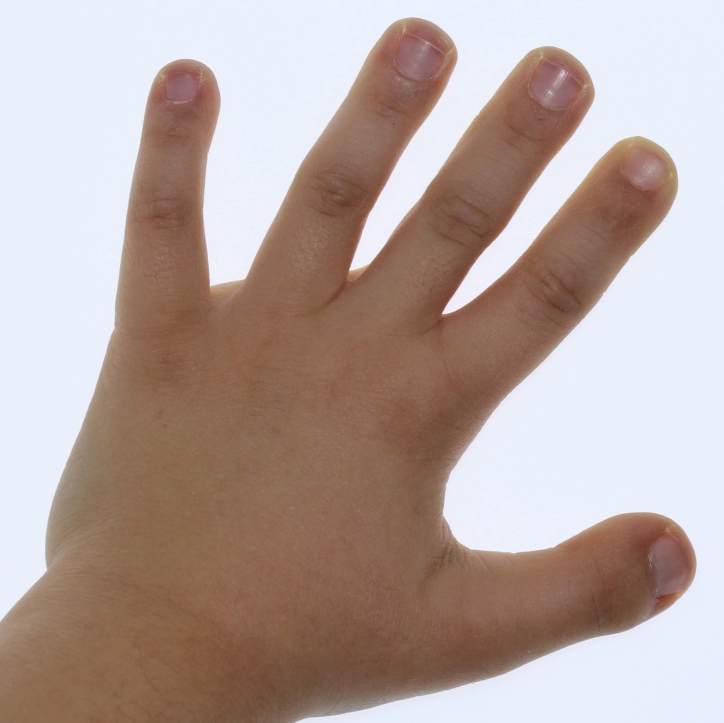
![Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114458/bin/fhs-Image002.jpg) Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf01 abril 2025
Figure 2. [Dorsal (A) and palmar (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf01 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials01 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials01 abril 2025 -
 The behavioral phenotype of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: A scoping review of the literature - Awan - 2022 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library01 abril 2025
The behavioral phenotype of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: A scoping review of the literature - Awan - 2022 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library01 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS)01 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS)01 abril 2025 -
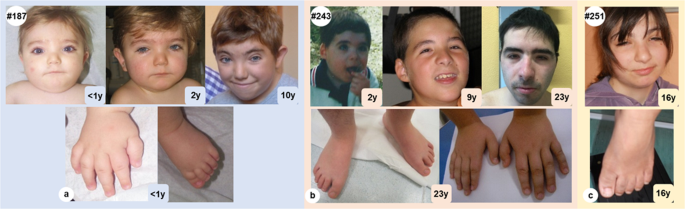 Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping01 abril 2025
Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping01 abril 2025 -
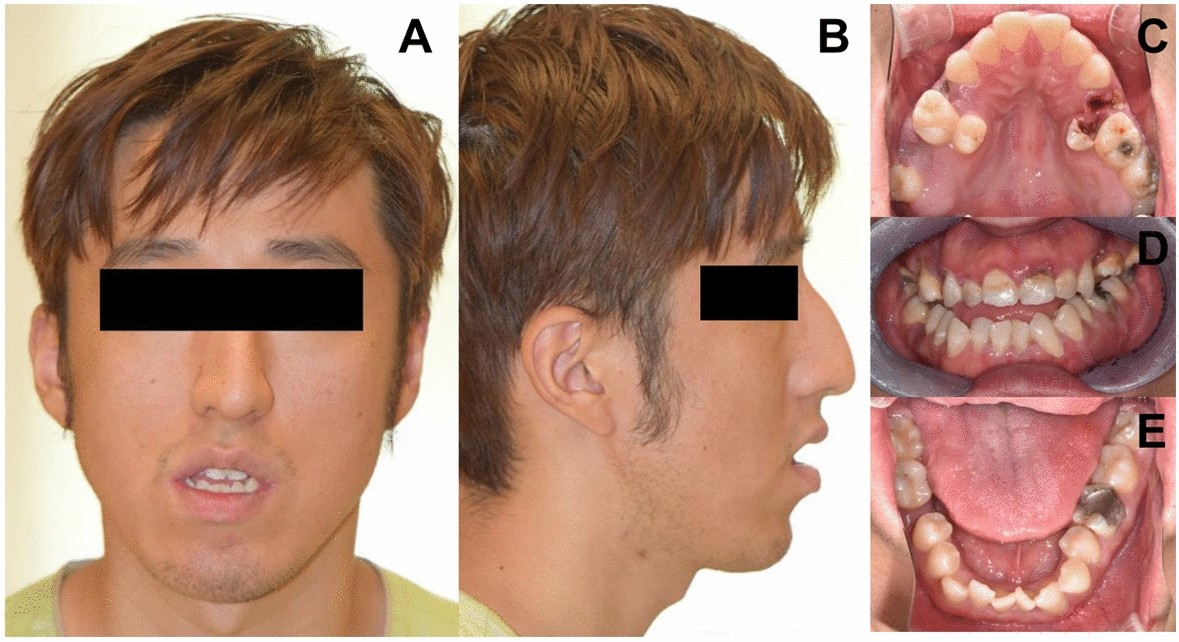 Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient01 abril 2025
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient01 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: principal oral and dental disorders and literature update01 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: principal oral and dental disorders and literature update01 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Campeão em 2000, Rincon aconselha compatriotas no Mundial de01 abril 2025
Campeão em 2000, Rincon aconselha compatriotas no Mundial de01 abril 2025 -
 🔥 Somali and the Forest Spirit MBTI Personality Type - Anime & Manga01 abril 2025
🔥 Somali and the Forest Spirit MBTI Personality Type - Anime & Manga01 abril 2025 -
 Jogo Dominó 28 Peças Resina Branco Estojo Armazena Qualidade01 abril 2025
Jogo Dominó 28 Peças Resina Branco Estojo Armazena Qualidade01 abril 2025 -
 I Love You. Russian Language. Vector Watercolor Splash Paint Royalty Free SVG, Cliparts, Vetores, e Ilustrações Stock. Image 63954375.01 abril 2025
I Love You. Russian Language. Vector Watercolor Splash Paint Royalty Free SVG, Cliparts, Vetores, e Ilustrações Stock. Image 63954375.01 abril 2025 -
 Jogo do Galo ou Jogo da Velha (card 13x10cm)01 abril 2025
Jogo do Galo ou Jogo da Velha (card 13x10cm)01 abril 2025 -
 Dólar fecha no maior valor da história do Plano Real - Tribuna do01 abril 2025
Dólar fecha no maior valor da história do Plano Real - Tribuna do01 abril 2025 -
 Thor: Love and Thunder' Off to a Godly Start at the Domestic Box Office - Murphy's Multiverse01 abril 2025
Thor: Love and Thunder' Off to a Godly Start at the Domestic Box Office - Murphy's Multiverse01 abril 2025 -
 JOGO DO BICHO RESUMO DAS PRIMEIRAS AULAS-JOGODOBICHO01 abril 2025
JOGO DO BICHO RESUMO DAS PRIMEIRAS AULAS-JOGODOBICHO01 abril 2025 -
 Meus pokemons favoritos do tipo água grama e fogo01 abril 2025
Meus pokemons favoritos do tipo água grama e fogo01 abril 2025 -
 MPPI - Ministério Público do Estado do Piauí01 abril 2025
MPPI - Ministério Público do Estado do Piauí01 abril 2025