Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: clinical features, genetic basis
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 06 abril 2025
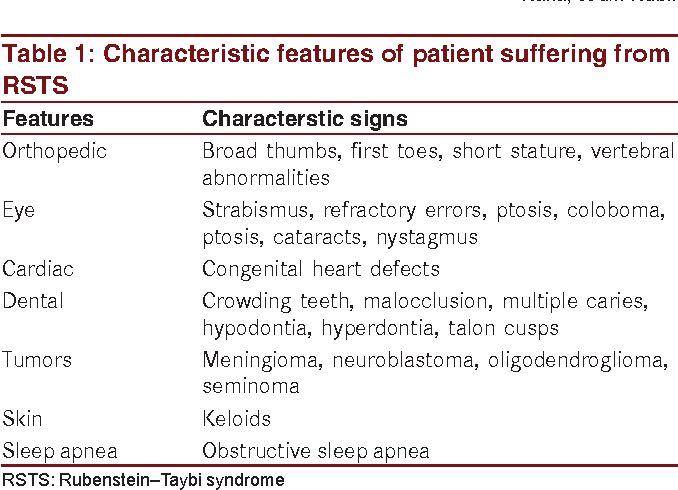
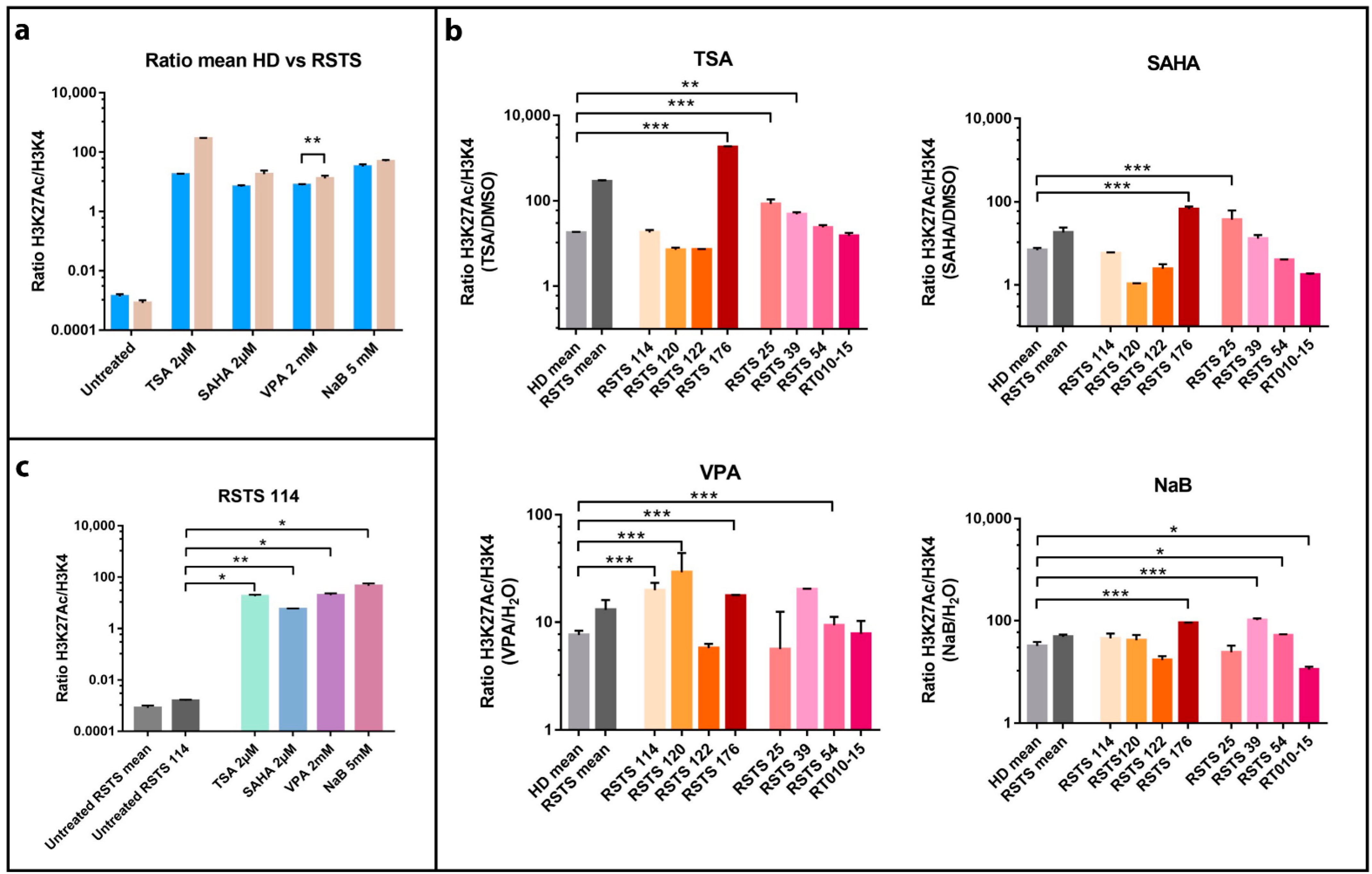
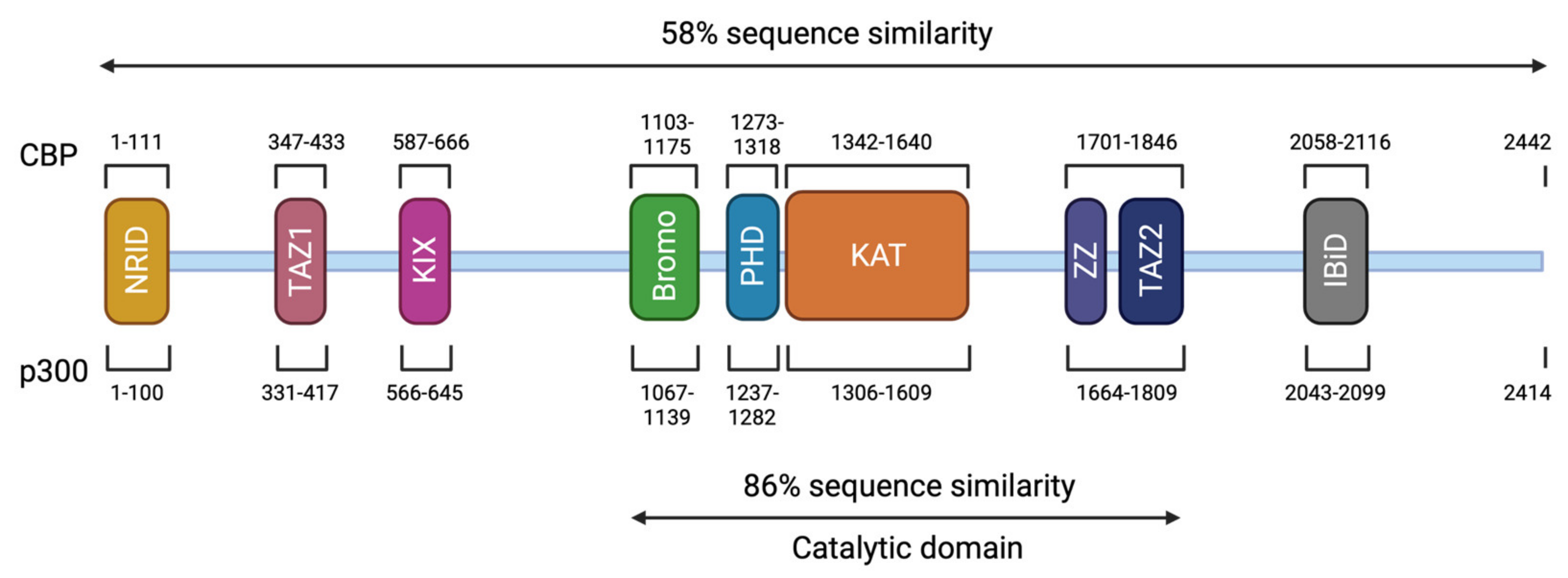
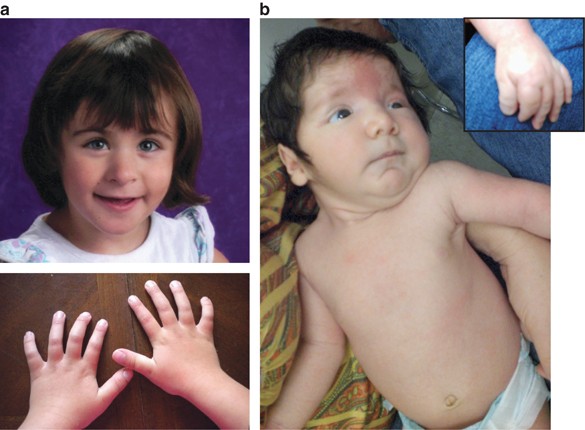
Background Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic disease, with an estimated prevalence of one case per 125,000 live births. RSTS is characterized by typical facial features, microcephaly, broad thumbs and first toes, intellectual disability, and postnatal growth retardation. However, no standard diagnostic criteria are available for RSTS. In this review, we summarized the clinical features and genetic basis of RSTS and highlighted areas for future studies on an appropriate diagnostic protocol and follow-up care for RSTS. Discussion RSTS is primarily characterized by delayed growth in height and weight, microcephaly, dysmorphic facial features, and broad thumbs and big toe. Over 90% RSTS individuals with disabilities survive to adulthood, but healthcare for these patients is particularly complex, time-consuming, and costly. In addition, no standard diagnostic criteria and follow-up care guidelines are available for RSTS. It has been shown that mutations in the genes encoding the cyclic-AMP-regulated enhancer binding protein (CREBBP) and the E1A-binding protein p300 (EP300) contributed to the development of RSTS. Therefore, genetic tests are useful for the diagnosis of RSTS, although most RSTS cases are currently diagnosed based on clinical features. Summary The clinical features of RSTS have been extensively studied, which significantly contributes to the diagnosis of this extremely rare syndrome. However, the pathogenesis and genotype-phenotype associations of RSTS are largely unknown. Therefore, multicenter studies and international cooperation are highlighted for better understanding of this disease, establishing standard diagnostic criteria, and providing professional management and follow-up care of RSTS.

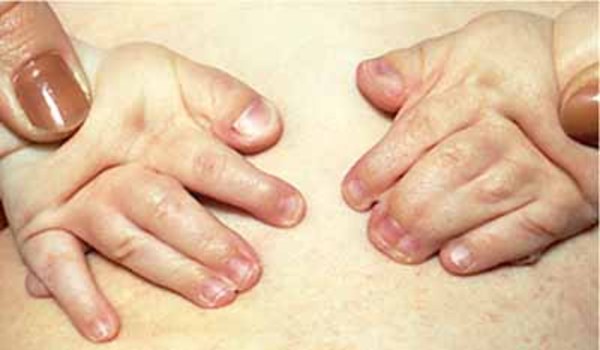
Images showing classical RSTS features of patient including
From Diagnosis to Management : Rubinstein – Taybi Syndrome

Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo

a,b: Patient A at 3 weeks; c,d: Patient B at 6 weeks, note the

Clinical photos of the patients. (a) Case 1: Dysmorphic facial
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome OMIM# 180849 - FDNA™
Genes, Free Full-Text
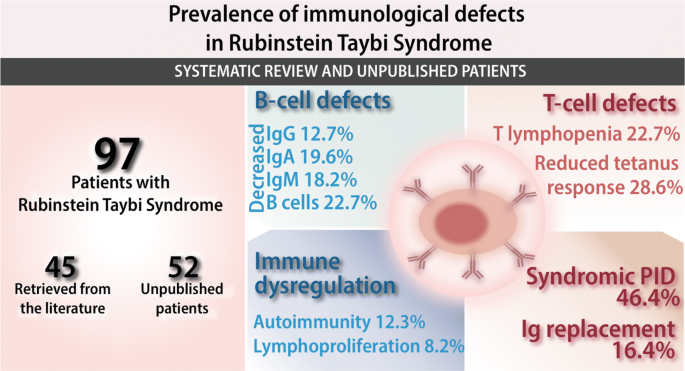
Prevalence of Immunological Defects in a Cohort of 97 Rubinstein

Fetal phenotype of Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome caused by CREBBP

Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome in a Filipino Infant with a Novel CREBBP
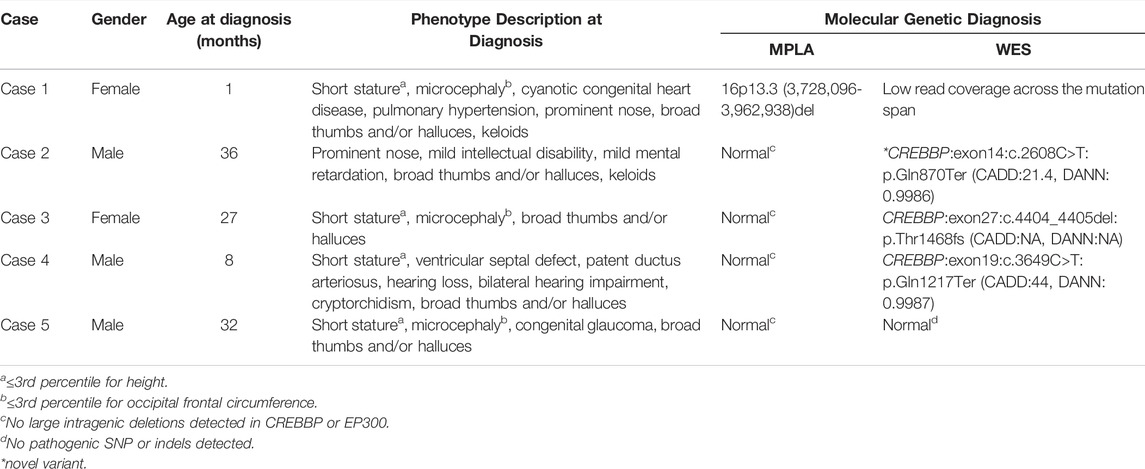
Frontiers Genetic Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome With
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics

Main clinical findings of the 16 Brazilian patients with
Recomendado para você
-
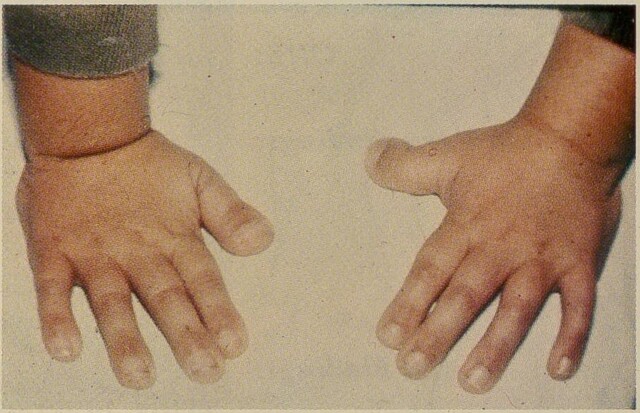 What Is Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome? - StoryMD06 abril 2025
What Is Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome? - StoryMD06 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A case report06 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A case report06 abril 2025 -
 Exon deletions of the EP300 and CREBBP genes in two children with06 abril 2025
Exon deletions of the EP300 and CREBBP genes in two children with06 abril 2025 -
 Silas : Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome » SWEET NECTAR SOCIETY06 abril 2025
Silas : Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome » SWEET NECTAR SOCIETY06 abril 2025 -
Dentocyclopedia - rubinstein taybi syndrome06 abril 2025
-
 Psychiatric Profile in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome06 abril 2025
Psychiatric Profile in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome06 abril 2025 -
 SÍNDROME DE RUBINSTEIN-TAYBI - CANAL INFANTIL06 abril 2025
SÍNDROME DE RUBINSTEIN-TAYBI - CANAL INFANTIL06 abril 2025 -
 Guapimirim News: CRIANÇAS ESPECIAIS 12 - Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi06 abril 2025
Guapimirim News: CRIANÇAS ESPECIAIS 12 - Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi06 abril 2025 -
 O que é síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi? - Crianças Especiais06 abril 2025
O que é síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi? - Crianças Especiais06 abril 2025 -
 Día Internacional del Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi: Una jornada para crear conciencia06 abril 2025
Día Internacional del Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi: Una jornada para crear conciencia06 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 A whole slew of new games are available for September's Prime Gaming offerings — GAMINGTREND06 abril 2025
A whole slew of new games are available for September's Prime Gaming offerings — GAMINGTREND06 abril 2025 -
 Honkai Star Rail: What is the current banner & who will be next06 abril 2025
Honkai Star Rail: What is the current banner & who will be next06 abril 2025 -
 The Callisto Protocol: Artista brasileiro fala sobre pressão e comparações com Dead Space - NerdBunker06 abril 2025
The Callisto Protocol: Artista brasileiro fala sobre pressão e comparações com Dead Space - NerdBunker06 abril 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/puff_l-3-0a154477191b4d599810b7b4fa119723.jpg) Sean Combs sheds his ''Puff Daddy'' moniker06 abril 2025
Sean Combs sheds his ''Puff Daddy'' moniker06 abril 2025 -
 Camiseta Personalizada Stumble Guys Infantil Games Jogo06 abril 2025
Camiseta Personalizada Stumble Guys Infantil Games Jogo06 abril 2025 -
![X Marks The Spot in under 2 minutes! - [Speedrunning Quest Guide OSRS]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/e5iZq1ixvok/maxresdefault.jpg) X Marks The Spot in under 2 minutes! - [Speedrunning Quest Guide OSRS]06 abril 2025
X Marks The Spot in under 2 minutes! - [Speedrunning Quest Guide OSRS]06 abril 2025 -
 IHOP to close nearly 100 underperforming restaurants - TODAY06 abril 2025
IHOP to close nearly 100 underperforming restaurants - TODAY06 abril 2025 -
 – Push it sideways!06 abril 2025
– Push it sideways!06 abril 2025 -
Jogo de Sinuca Online06 abril 2025
-
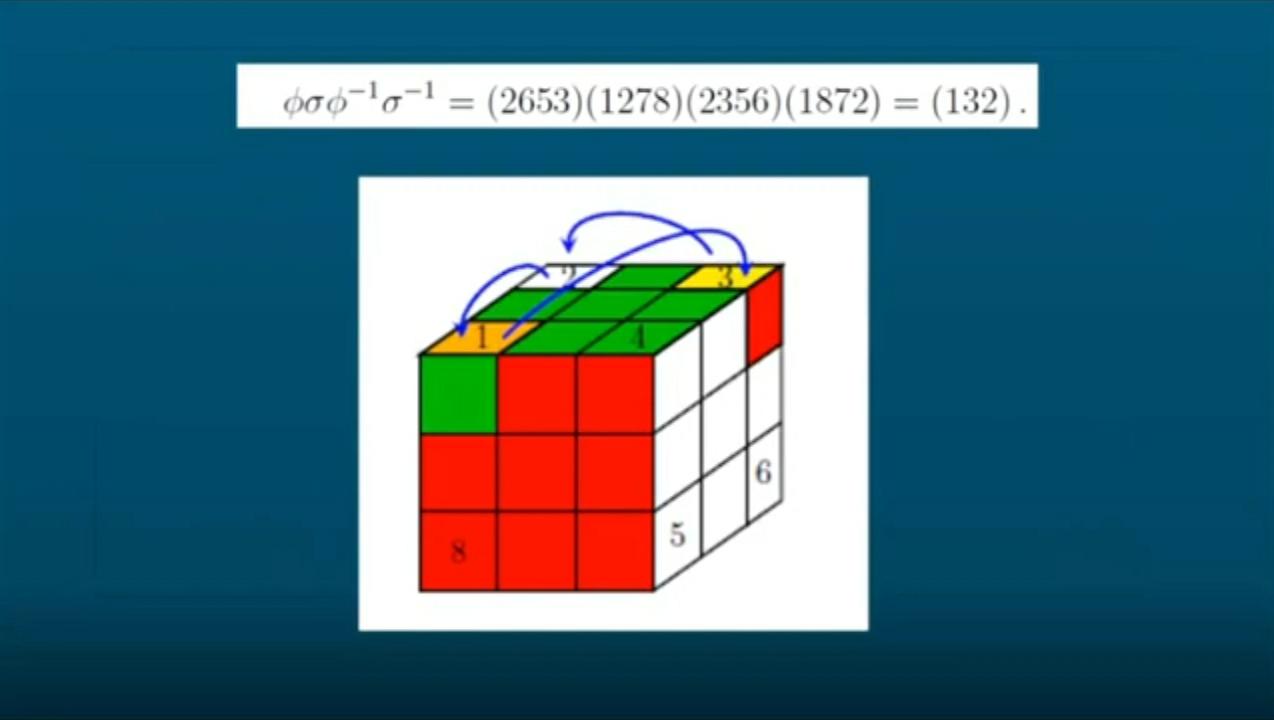 6754 MD – Cubo mágico e Teoria de Grupos06 abril 2025
6754 MD – Cubo mágico e Teoria de Grupos06 abril 2025

